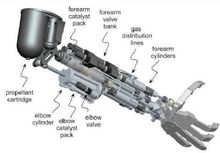
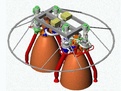
Eaton Char-Lynn Motor – Rocket Motor, 3 Acoustic Phenome
The Eaton Char-lynn Motor says that the extreme vibration and acoustic environment within the rocket motor causes its peak stress to be much higher than the average, especially for the organ resonance and airflow disturbances. Explain the acoustic phenomena of the following three rocket motors.
Unstable combustion
There are several types of combustion instability:
Intermittent combustion
This is the low frequency vibration of the combustion chamber pressure caused by changes in the propellant delivery tube caused by changes in the acceleration of the carrier. The carrier thrust can be periodically changed, resulting in damage to the load and the carrier. Intermittent combustion can be prevented by using a high density propellant with an aerated damping turbo pump.
Cicada phenomenon
This is due to insufficient pressure in the propellant injector. It is mainly unpleasant and has no substantial harm. However, in some extreme cases, combustion may enter the injector, causing an explosion of the unit propellant.
Oscillating combustion
This situation often causes direct damage and is difficult to control. It is often an acoustic process that accompanies the chemical combustion process and is the main driving force for energy release. Can lead to unstable resonance, thinning the insulating boundary layer, with tragic consequences. This effect is difficult to pre-analyze at the design stage, only through protracted testing, and is constantly revised. Modifications typically include fine-tuning the ejector, changing the chemistry of the propellant, or evaporating into a gaseous state before spraying the propellant into the Helmholtz damper (to change the resonance state of the combustion chamber).
Another common test method is to detonate a small amount of explosive in the combustion chamber to determine the impulse response of the motor and estimate the response time of the chamber pressure: the faster the recovery, the more stable the system.
Exhaust noise
Rocket motors (except for small ones) are very noisy compared to other motors. The supersonic exhaust gas mixes with the surrounding air to form a shock wave. The sound intensity of the shock wave depends on the size of the rocket.
When Saturn V was launched, it was detected by a seismometer far from its launch point. The resulting sound intensity depends on the size of the rocket and the speed of the exhaust. The shock wave characteristic sound heard at the scene is mainly a popping sound. This noise peak exceeds the permissible upper limit of the microphone and audio electronics, so this noise is attenuated or disappeared during recording or broadcast audio playback. The noise of a large rocket launch can directly kill people around. The noise around the base when the space shuttle took off exceeded 200dB (A).
Usually the rocket is the most noisy near the ground because the noise radiates out of the plume and is reflected by the ground. Also, when the carrier slowly rises, only a small amount of propellant energy is converted into the kinetic energy of the carrier (the useful work P is transferred to the carrier P=F*V, F is the thrust, and V is the speed), so most of the energy is dispersed. In the exhaust gas, it interacts with the surrounding air to generate noise. This noise can be reduced by a top flame isolation slot that sprays water to the plume and deflects the plume angle.
learned that the implementation plan for the improvement of China’s motor energy efficiency is as follows:
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Notice of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine on Organizing the Implementation of the Motor Energy Efficiency Improvement Plan (2013-2015)
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology [2013] No. 226 provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the Central Government and cities with separate plans, Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Industrial and Information Management Department, Quality and Technical Supervision Bureau, relevant central enterprises: to implement the “12th Five-Year Plan” energy conservation and emission reduction plan And the industrial energy conservation “Twelfth Five-Year Plan” to improve the energy efficiency of the motor and promote the upgrading of the motor industry. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine organized the “Electrical Energy Efficiency Improvement Plan (2013-2015)”, which is printed and distributed to you. The relevant organizational implementation requirements are as follows:
First, pay close attention to organize the development of motor system energy-saving renovation plan
All regions should organize industrial enterprises to eliminate the roadmap for the elimination of motor energy efficiency improvement plan, carry out self-examination (see Annex 2), and guide key enterprises to formulate energy-saving retrofits and elimination of backward systems for motor systems in 2013-2015, and support enterprises to select high-efficiency motor replacement. Effective motor, matching transformation of motor and dragging equipment. Key enterprises with annual power consumption of 10 million kWh and above (the local areas can expand the scope of key enterprises according to actual conditions) should report the motor system energy-saving renovation plan (see Annex 3) as required, and report it to the provincial industrial and information administration department for review. Summary and archiving. The provincial industrial and information administration departments are required to submit the motor system energy efficiency improvement plan summary table (Annex 4) to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology before the end of September. The competent departments of industry and informatization at all levels shall strengthen supervision and inspection, conduct key inspections on enterprises that are not serious in self-examination and whose energy-saving transformation plans are not clear, and guide enterprises to formulate three-year transformation and elimination of backward programs as required.
Second, conscientiously organize motor manufacturing enterprises to enforce mandatory performance standards
All regions shall organize motor production enterprises in their respective administrative regions to conduct self-inspection against the national standard (GB18613-2012) for energy efficiency limit and energy efficiency rating of small and medium-sized three-phase asynchronous motors, and guide enterprises according to the overall requirements for the compliance of all motor products before the end of 2013. Develop a compliance plan and accelerate organizational implementation. The motor manufacturer shall report to the self-inspection form of the basic situation of the motor manufacturer (see Annex 5) and report it to the provincial competent department of industrial and information technology and quality and technology supervision. The competent departments of industrial and information technology and quality and technology supervision at all levels shall submit the summary plan of the motor production enterprise compliance plan (Annex 6) to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine before the end of August. Before the end of 2013, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine will organize special inspections on the implementation of energy efficiency standards and labeling, and will adopt public exposure and other penalties for enterprises that fail to meet the standards.
Third, the preparation of motor efficient remanufacturing pilot program
In Shanghai, Anhui, Shaanxi, Hunan, Jiangxi and other provinces and cities, it is necessary to speed up the preparation of a pilot program for efficient motor remanufacturing. The pilot program should focus on building a standardized waste motor recycling system, cultivating large-scale motor efficient remanufacturing demonstration projects, improving the level of remanufacturing technology, and strengthening the quality control of remanufactured products, setting targets and tasks, formulating specific measures, and clearly supporting policies. , strengthen safeguard measures. The above-mentioned regions will be invited to report to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology before the end of September 2013.
Fourth, recommend a batch of advanced and applicable motor technology
https://www.xjetl.com.com