Eaton Char-Lynn Motor – Star Motor Motor Operation
A star motor is a reciprocating internal combustion motor in which cylinders are arranged around a crankshaft. Before the advent of turbine motors, most large aircraft motors were star-shaped.
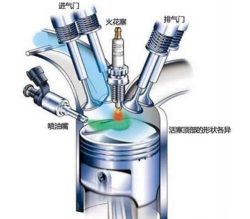
The Eaton Char-lynn Motor states that in a star motor, the piston is connected to the crankshaft via a main connecting rod. The connecting rod connected to the uppermost piston is the main link. The connecting rods of other pistons are referred to as articulated links, which are connected by a tip hole to a ring at the center of the main link.
The star motor has high reliability, light weight, great potential for power improvement, and good maintainability and survivability. The number of cylinders of a typical star motor is an odd number. There are 5 cylinders, 7 cylinders and 9 cylinders. The multi-row stacking is arranged in several rows, and the maximum number of cylinder groups can be up to 4 rows x 7 cylinders, and the Pu-Hui company’s giant wasp R-4360 reaches 28 cylinders.
Before the advent of jet motors, most of the piston aircraft motors used star-shaped designs. Because of their strong short-field survival, they were widely used by carrier-based aircraft because of their compact structure and small aircraft space. The rest of the motors were V-shaped. Some modern light aircraft use inline or horizontally opposed motors.
motor operation:
Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the links cannot all be directly connected to the crankshaft unless a mechanically complex splitter link is used, none of which is successful. Instead, the piston is connected to the crankshaft through the main articulated rod assembly.
The four-stroke radial cylinders have an odd number of cylinders per row, thus maintaining a consistent firing sequence for every other piston, providing smooth operation. For example, on a five-cylinder motor, the firing sequence is 1, 3, 5, 2, 4 and returns to cylinder 1. Furthermore, this always leaves a single piston clearance between the piston during its combustion stroke and the compression of the piston. The effective stroke directly helps to compress the next cylinder, making the movement more uniform. If an even number of cylinders are used, the same timing ignition cycle is not feasible.
Star motors typically use fewer cam lobes than other types. As with most four strokes, the crankshaft requires two revolutions to complete the four strokes (intake, compression, combustion, exhaust) of each piston. The cam collar rotates at a slower speed and is opposite the crankshaft. The cam blades are placed in two rows for intake and exhaust. For example, four cam lobes are used for all five cylinders, while a typical inline motor with the same number of cylinders and valves requires 10 cam lobes.
Most radiant motors are driven by push rods and tappets on cam discs that are concentric with the crankshaft.
Overhead poppet valves with some smaller radials, such as the Kinner B-5 and the Russian Shvetsov M-11, use separate camshaft cylinders in the crankcase.
https://www.xjetl.com