Mastering Magnetism: The Rising Influence of Thin Block NdFeB Magnets
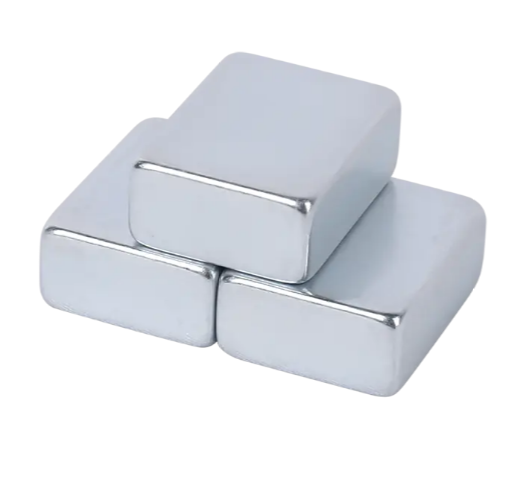
The interconnected realms of science, engineering, and technology have reaped enormous benefits from understanding and harnessing the incomparable power of magnetism. Among the various kinds of magnet technologies commercially available, a particular subset—Thin Block Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) Magnets(https://www.mlmagnet.com/product/ndfeb-magnet/ndfeb-block-square-magnets/)—has emerged as a game-changer due to its exceptional properties. Thin Block NdFeB Magnets are the strongest type of rare earth magnet commercially available. They are also known as Neo, Neod, or NIB magnets.
The thin block NdFeB magnets are a specialized variety of these magnets, tailored to cater to specific applications which demand high magnetic field in a compact package. The thin block NdFeB magnets provide a host of advantages due to their specific features. One of the principal advantages they bring aboard is their incredible power. Despite their compact size, these magnets provide a very high magnetic field—much greater than that generated by many other types of magnets. This unparalleled strength stems from the use of Neodymium, a rare-earth metal.
This metal, when combined with iron (Fe) and boron (B), produces a potent magnetic pull that is quite impressive. Along with their compact size and dominant strength, thin block NdFeB magnets also boast a series of other compelling features, such as higher coercivity and remanence. Thin Block NdFeB Magnets greater coercivity means that they can withstand higher levels of reverse magnetic field without demagnetization. On the other hand, the greater remanence indicates that these magnets can retain a greater level of magnetism after being magnetized once, thus ensuring a longer lifespan. Apart from their magnetic characteristics, thin block NdFeB magnets also possess high resistance to demagnetization, outstanding energy products, and incredible performance per unit of cost.
Some grades can operate at temperatures up to 200°C, expanding their range of applications. Today, thin block NdFeB magnets have found applications in myriad areas, from the complex domains of aerospace and robotics to more common household appliances. They are commonly used in hard disk drives, speakers, electric motors, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines, and numerous other applications. Their thin and compact size makes them perfect for applications where space is a constraint, but the requirement for a strong magnetic field is high. However, like any other product, these magnets also come with their set of caveats. Since they are composed of a combination of Neodymium, iron, and boron, they are prone to corrosion. Appropriate coatings or platings are generally used to make these magnets corrosion-resistant. Also, they are brittle and can chip or break if mishandled.
Despite their minor drawbacks, thin block NdFeB magnets have proven themselves as a substantially transformative force in today’s technologically advanced world. Their superior magnetic characteristics, coupled with high versatility and cost-effectiveness, make them a popular choice for varied applications across different industries. The world of magnetism is complex, but it is also undeniably captivating. As we continue to dive into its depths, thin block NdFeB magnets emerge as a significant player in the arena. They teach us that we can extract immense power from compact packages, propelling us forward in our journey of technological development.
In the end, it is innovations like thin block NdFeB magnets that challenge our perceptions, striving for powerful solutions in compact packages in the expanding landscape of modern technology. Their proposition carries with it a promise of the future, where we will be able to achieve even more with lesser and lesser resources.