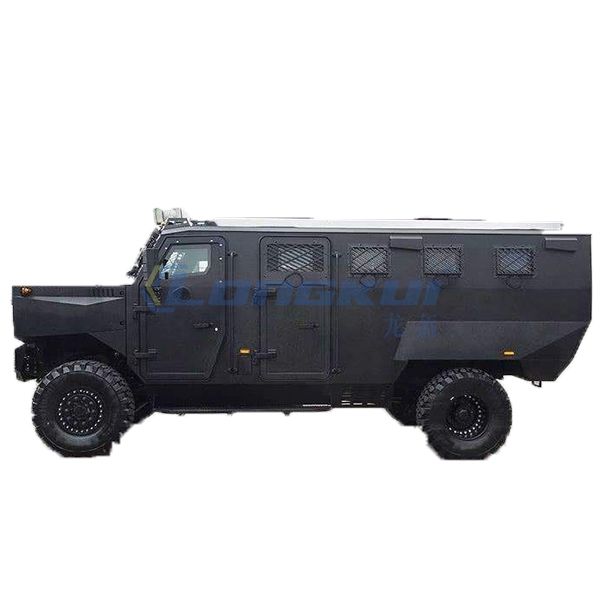
Military Car, Ship Amor Plate made from UD Protective Composite Fabric
Key features of UD protective composite fabric may include:
Ballistic Resistance: These fabrics are often used in the construction of body armor and other protective gear to provide resistance against bullets and other ballistic threats. The unidirectional fiber orientation helps to dissipate the energy of the projectile, reducing the risk of injury to the wearer.
Stab and Puncture Resistance: UD fabrics can be designed to resist stabbing and puncture threats, making them suitable for protective clothing, such as stab-resistant vests or gloves.
Fragmentation Protection: They can also be used to protect against fragments from explosive devices, which is particularly important in military and law enforcement applications.
Lightweight and Flexible: UD protective fabrics are typically lightweight and flexible, which is crucial for applications where wearers need to maintain mobility and comfort.
Composite Construction: These fabrics are often composed of multiple layers, each with a specific function. For example, a ballistic-resistant fabric may consist of multiple layers of UD materials, as well as additional layers for back face deformation reduction and comfort.
Material Selection: The specific materials used in UD protective composite fabrics may vary but often include high-strength fibers such as aramids (e.g., Kevlar) or ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE).
Layering and Lamination: The layers of UD fabric can be combined using lamination or other bonding techniques to create a composite material with superior protective properties.
UD protective composite fabrics play a critical role in personal protective equipment (PPE), military applications, and law enforcement gear, as they offer a balance of protection and comfort. Manufacturers continuously work to improve the performance and design of these materials to meet the evolving needs of various end-users.