What is limb lengthening?
What is Limb lengthening?
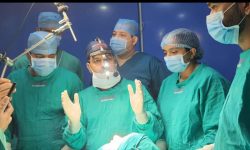
Limb lengthening is a surgical procedure used to increase the length of a bone in the arms or legs. This procedure is typically performed to correct limb length discrepancies (LLDs), where one limb is shorter than the other, or to address congenital conditions, injuries, or bone deformities that have resulted in limb shortening.
The limb lengthening process involves three main stages:
Surgical Procedure: The bone is surgically cut in a procedure called osteotomy. A device, such as an external fixator or internal lengthening nail, is then attached to the bone to stabilize it and gradually lengthen it over time.
Distraction Phase: During this phase, the device is adjusted regularly to gradually pull the bone segments apart. This process stimulates the body’s natural bone healing response, leading to the formation of new bone tissue in the gap.
Consolidation Phase: After the desired length is achieved, the bone segments are allowed to consolidate and heal. This phase is crucial for ensuring the new bone is strong enough to bear weight.
Limb lengthening procedures can be performed on the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), humerus (upper arm bone), or other bones in the arms or legs, depending on the specific needs of the patient. The lengthening process is typically slow and gradual, with the rate of lengthening controlled to minimize complications and ensure optimal healing.