How Virtual Machine works
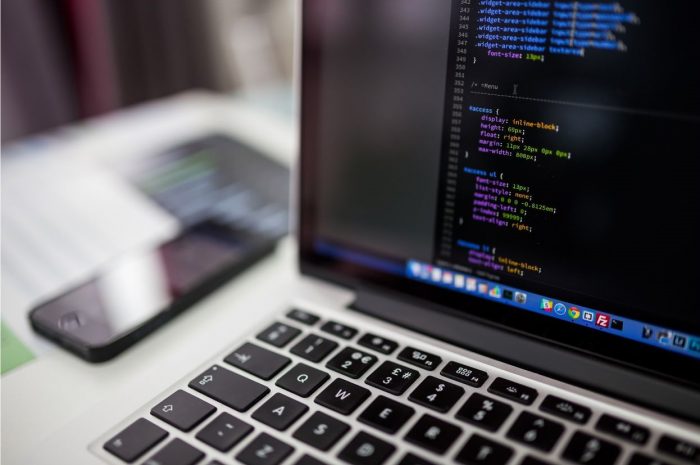
In this blog post, how virtual machine works? we explained in detail. (VMs) are software-based emulations of physical computers allow multiple OS. and the running of programs on a single physical system. They establish an abstraction layer between the guest operating systems and the underlying hardware, resulting in a virtualized environment where each VM can function independently. How Virtual Machine works
Introduction
Virtualization technology has evolved to provide enhanced performance, improved hardware support, advanced management tools, and increased flexibility. Virtual machines have become integral to modern IT infrastructure, supporting a wide range of applications, from server consolidation to software development and testing, and powering the cloud computing revolution.
By leveraging virtualization technology, virtual machines enable better utilization of hardware resources, cost savings through consolidation, simplified management and deployment, enhanced security through isolation, and increased flexibility in software development and testing. Virtual machines have become a fundamental building block in modern computing environments, empowering organizations to optimize their infrastructure and improve operational efficiency.
How Virtual machine works?
We explained in detail how virtual machine works,
How virtual machine works? Virtualization is the process of building a software-based, or “virtual,” version of a computer with dedicated resources from a physical host computer, such as your personal computer, and/or a a distant server, such one located in the datacenter of a cloud service provider. A virtual machine is a computer file, often known as an image, that functions like a real computer.
i0.wp.com
An operating system and an application are packaged along with information about the CPU, memory, storage, networking, and other computing resources that are required to run them in a virtual machine. A program known as a hypervisor examines the description before supplying the needed compute resources when this virtual machine is installed on a host computer.
On the same host computer, many virtual machines—even ones with various operating systems—can operate independently and concurrently.
Virtual machine-based systems are created to increase a host’s effectiveness. The system’s fine-grained resource parsing gives it extensive insight into systems. Additionally, these platforms give app-specific insights regarding costs, performance, resource usage, and development procedures. This is how virtual machine works information covers.
Best Virtual machine platforms
The “best” virtual machine platform depends on your specific needs, requirements, and the operating system you’re using. Each virtual machine platform has its own strengths and considerations. Here are some popular virtual machine platforms and their key characteristics:
- VMware Workstation: VMware Workstation is known for its comprehensive feature set and robust performance. It offers advanced capabilities for developers and IT professionals, such as snapshots, cloning, remote access, and integration with VMware’s ecosystem. It supports a wide range of guest operating systems and provides excellent compatibility. However, it is a commercial product with a cost associated with it.
- Oracle VM VirtualBox: VirtualBox is a popular choice for individual users and small-scale virtualization needs. IIt is open-source and free, making it available to a variety of people. VirtualBox supports various guest operating systems, offers solid performance, and has a user-friendly interface. However, it may not have the same level of advanced features and enterprise-grade support as commercial solutions.
- Microsoft Hyper-V: Hyper-V is a native hypervisor for Windows-based systems. It is widely used in enterprise environments and integrates well with Microsoft’s ecosystem, including Windows Server and Azure cloud services. Hyper-V provides good performance and scalability and offers features like live migration, high availability, and integration with Windows management tools. However, it is available only on specific editions of Windows and may have more limited compatibility with non-Windows guest operating systems.
- KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine): KVM is an open-source virtualization solution integrated into the Linux kernel. It provides solid performance and is widely used in Linux-based environments. KVM leverages hardware virtualization extensions and offers robust management capabilities. However, it requires a Linux host system and may have a steeper learning curve for configuration and management.
The best virtual machine platform for you depends on factors such as your specific requirements, budget, guest operating system support, performance needs, and level of technical expertise. It’s recommended to evaluate the features, compatibility, performance, support, and cost of different platforms to determine the best fit for your use case.
Conclusion
In conclusion, how virtual machines works (VMs) work by leveraging software-based virtualization to create an isolated and independent environment for running operating systems and applications. The key elements of how virtual machines work include the hypervisor, resource allocation, guest operating system installation, hardware abstraction, hypervisor interaction, resource management, isolation and security, and VM monitoring and management.