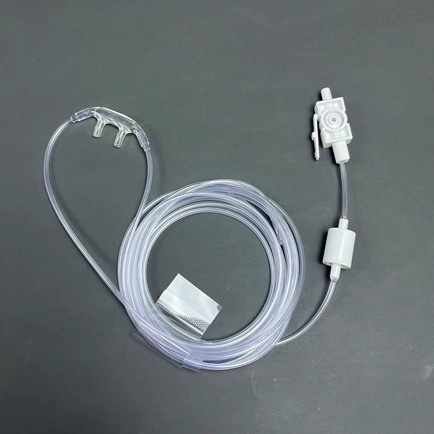
Nasal Cannula Sampling Line
As a specific type of sampling line used in capnography monitoring, the nasal cannula sampling line consists of a nasal cannula attached to a tubing system that connects to a capnography monitor or analyzer.
This type of sampling line is used when monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2) levels in patients through the exhaled breath. The nasal cannula is placed in the patient’s nostrils, allowing for the sampling of respiratory gases and providing real-time data on the patient’s CO2 levels during anesthesia or ventilation procedures.
Types of Nasal Cannula Sampling Line
R-Type Nasal Cannula Sampling LineConnected to the air circuit, collect the moisture in the nasal exhalation, and adapt to the R series EtCO2 sensor. Single use consumables. Various specifications and models are available to suit different equipment and types of patients.
R-Type Nasal Cannula Sampling Line
M-Type Nasal Cannula Sampling LineConnect to the gas circuit, collect the moisture in the nasal exhalation, and adapt to the M series EtCO2 sensor. Disposable consumables. Various specifications and models are available to suit different equipment and types of patients.
M-Type Nasal Cannula Sampling Line
O-Type Nasal Cannula Sampling LineConnected to the air circuit, collect the moisture in the nasal exhalation, and adapt to the O series EtCO2 sensor. Single use consumables. Various specifications and models are available to suit different equipment and types of patients.
O-Type Nasal Cannula Sampling Line
Luer Nasal Cannula Sampling LineThe Luer Nasal Cannula Sampling Line is a medical device designed for efficient and comfortable collection of respiratory samples. It features a luer lock connector for secure attachment to monitoring…
Luer Nasal Cannula Sampling Line
What is the Nasal Cannula Method?
The nasal cannula method is used to deliver supplemental oxygen to a patient’s respiratory system. It involves the use of small, flexible tubes inserted into the patient’s nostrils, with the other end connected to an oxygen source. This method is commonly used in hospitals and home care settings.