• $1
DNase I Footprinting Assay
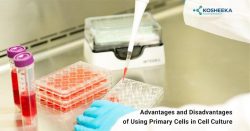
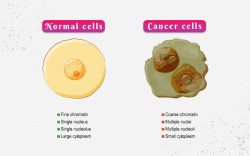
DNase I footprinting assay is a detection method that accurately identifies the binding sites of DNA binding proteins (such as transcription regulatory proteins) on DNA molecules. Transcription regulatory proteins regulate the transcription of target genes by binding to their promoter regions. At present, the EMSA (Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay) and DNase I footprinting assay are important sets of in vitro research tools. EMSA determines whether transcription factors are directly bound to DNA, while DNase I footprinting assay can accurately identify the DNA sequence to which they bind, thereby helping us to study the mechanism of gene transcription regulation.