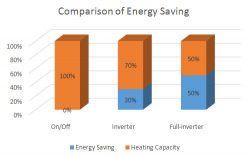
Inverter CPU
The 4–15 kw CPU is one of the inverter’s essential components, serving as the brain of the 4–15 kw inverter. Its primary duty is to transform the entire inverter into a programmable power system via circuit and program control.
The 18.5–400 kw cpu features reliable control logic processing capability as well as efficient computing and storage resources to assure the inverter’s reliability and stability. It can also automatically diagnose issues, assisting users in swiftly detecting and dealing with faults, enhancing production efficiency and device reliability.
Features of Inverter CPU
1. Processing Power: Inverter CPUs feature high processing power, capable of executing complex control algorithms and calculations with precision and speed.
2. Real-Time Control: With their advanced capabilities, inverter CPUs enable real-time control of motor parameters, allowing for precise speed, torque, and voltage regulation.
3. Communication Interfaces: Inverter CPUs are equipped with various communication interfaces, such as RS485, Ethernet, or CAN bus, allowing for seamless integration with other devices and systems in an industrial network.
4. Fault Detection and Diagnostics: Inverter CPUs incorporate fault detection algorithms and diagnostics capabilities to monitor the system’s health. They can detect anomalies, generate fault codes or alarms, and provide valuable diagnostic information for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes.
Real-time Control and Response with Inverter CPUs
Inverter CPUs have revolutionized the field of control and response in various industries. With real-time capabilities, these CPUs enable efficient and accurate monitoring, control, and response in a wide range of applications.
Real-time control refers to the ability of an inverter CPU to continuously monitor and adjust various parameters within a system in response to changing conditions. This allows for precise control over the output of the inverter, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. For example, in a solar power system, an inverter CPU can constantly monitor the amount of sunlight and adjust the power output accordingly, maximizing energy generation.
In addition to control, inverter CPUs also enable real-time response. This means that they can quickly analyze data and make necessary adjustments to ensure the system operates within desired parameters. For instance, in a manufacturing plant, an inverter CPU can detect equipment malfunctions or anomalies and respond immediately by shutting down the affected equipment or sending alerts to the operator.
Overall, real-time control and response with inverter CPUs offer several advantages. They improve system reliability by continuously monitoring and adjusting parameters. They also enhance energy efficiency by optimizing power output based on real-time conditions. Furthermore, the ability to quickly respond to anomalies or malfunctions minimizes downtime and improves overall productivity.
In conclusion, the incorporation of inverter CPUs with real-time control and response capabilities has significantly improved the efficiency, reliability, and productivity of various systems across industries. Their ability to monitor, control, and respond to changing conditions in real-time allows for optimal performance and enhanced user experience.