Other Materials Injection Molding
Other Materials Molding
Here we list some other materials for plastic injection molding parts.
PE, Polyethylene is a lightweight, durable thermoplastic with variable crystalline structure. It is one of the most widely produced plastics in the world. Polyethylene is used in applications ranging for films, tubes, plastic parts, laminates, etc. in several markets (packaging, automotive, electrical, etc.)
Polystyrene (PS) plastic is a naturally transparent thermoplastic that is available as both a typical solid plastic as well in the form of a rigid foam material. PS plastic is commonly used in a variety of consumer product applications and is also particularly useful for commercial packaging, laboratory ware, automotive, and Electronics.
General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) and High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) are probably the most commonly used PS resins for injection molding. GPPS is clear, but brittle (think of a CD jewel case) while HIPS is opaque and much less brittle.
Acrylonitrile Styrene (AS) – A group of copolymers that have the transparency of polystyrene, but with improved resistance to solvents and stress cracking. AS is used in applications ranging for Electrical/Electronic Applications, Appliances, Construction Applications, Decorative Parts, Automotive Applications, Piping, Telecommunications, Industrial Applications, Non-specific Food Applications.
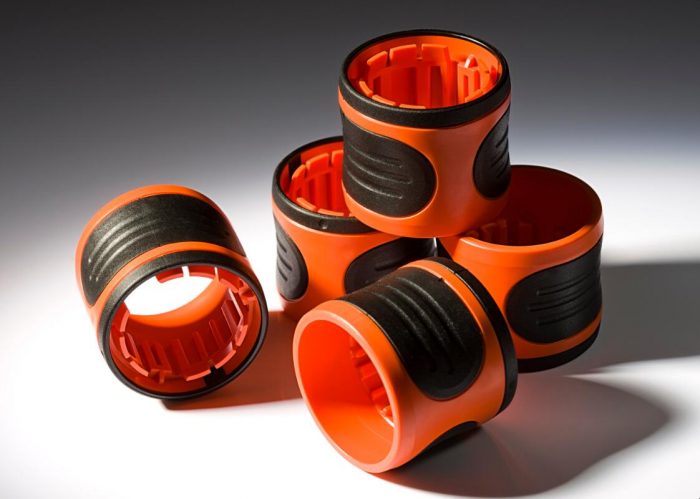
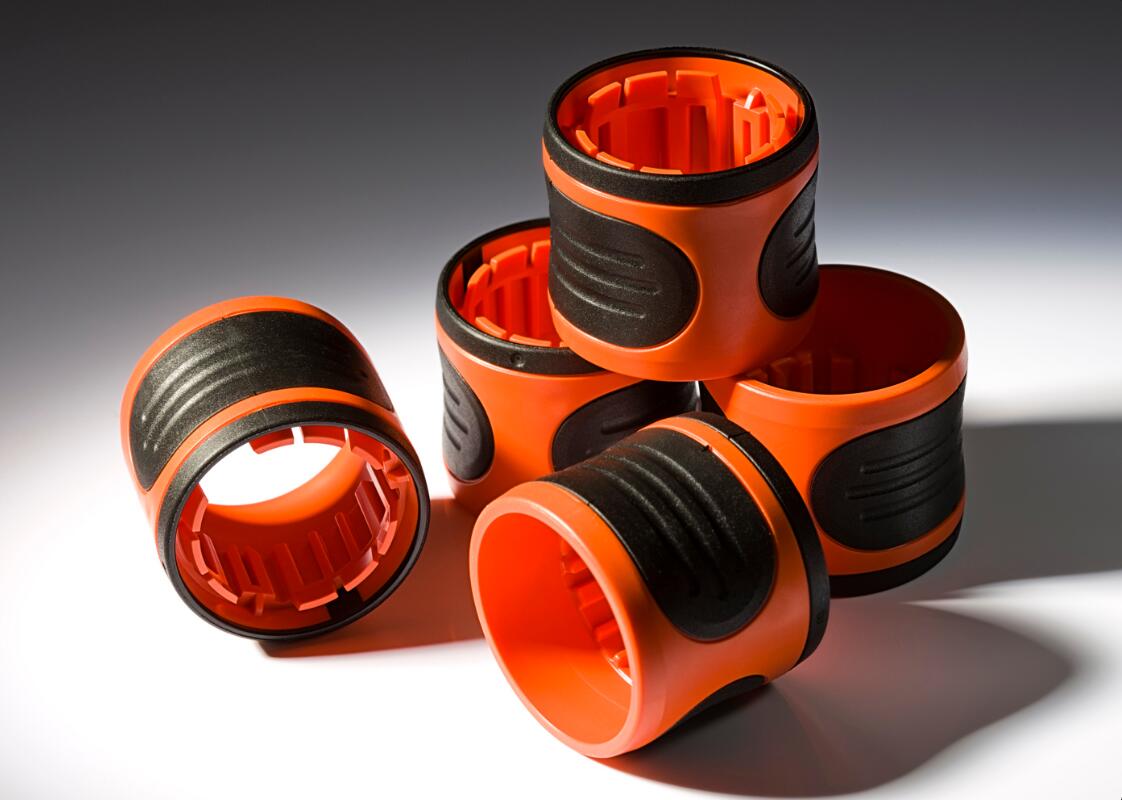
Thermoplastic Polyurethane or TPU is referred to as the bridge between rubbers and plastics. The material appears rubber-like, which means it can be extremely flexible, durable and smooth to the touch. All these properties and compound versatility makes TPU widely used in many industries for coatings, components and customer goods. TPU exhibits high-performance properties if processed correctly through injection molding, the important factors are mold and nozzle temperature, pressure and plasticizing energy. If the plastic injection molding process or an object’s design don’t suit the material, it may cause damage and shrinkage of parts.