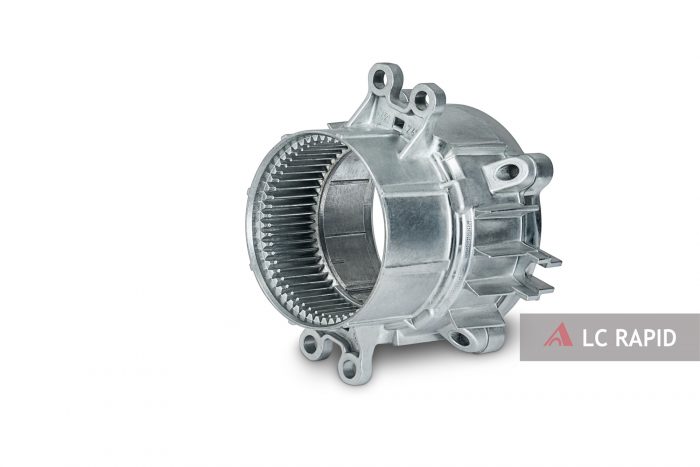
PROCESS FLOW AND APPLICATION OF DIE CASTING
Pressure die casting is a metal casting process, which is characterized by applying high pressure to the molten metal using the cavity of the mold. The die casting mold is usually processed with a higher strength alloy. Pressure die casting is particularly suitable for manufacturing a large number of small and medium-sized castings, so die casting is the most widely used one among various casting processes. Compared with other casting technologies, the die-casting surface is flatter and has higher dimensional consistency.
1. Design of Die Casting Mould
Die casting mold is an important process equipment in die casting production, and its design will directly affect the quality of die casting results.
The following points should be paid attention to when designing die casting mold:
(1) Use advanced and simple structure as much as possible to ensure stable and reliable operation and daily maintenance and repair.
(2) The modifiability of the gating system should be considered, and necessary modifications can be made during the debugging process.
(3) Reasonably select various tolerances, scales and machining allowances to ensure reliable mold fit and required die casting accuracy.
(4) Choose suitable mold materials and reliable heat treatment technology to ensure the service life of die-casting molds.
(5) It should have sufficient rigidity and strength to withstand the clamping pressure and expansion force without deformation during the die-casting production process.
(6) Use standardized die casting mold parts as much as possible to improve economy and interchangeability.
When designing the mold, it is necessary to calculate the total projected area and specific injection pressure during die-casting production according to the projected area of the casting to select a die-casting machine of suitable tonnage. The formula is as follows:
F expansion force = 100 P injection specific pressure × S projection area
F clamping force = F expansion force / K factor
2. Die casting process
The traditional die-casting process is mainly composed of four steps. The four steps include mold preparation, filling, injection, and sand falling. They are also the basis of various improved die-casting processes.
During the preparation process, a lubricant needs to be sprayed into the mold cavity. In addition to helping to control the temperature of the mold, the lubricant can also help demold the casting. Then you can close the mold and inject the molten metal into the mold with high pressure. The pressure range is about 10 to 175 MPa. When the molten metal is filled, the pressure will be maintained until the casting solidifies. Then the push rod will push out all the castings. Since there may be multiple cavities in a mold, multiple castings may be produced during each casting process. The process of falling sand requires separation of residues, including mold openings, runners, gates and flash. This process is usually done by extruding the casting with a special trimming die. Other methods of falling sand include sawing and sanding. If the gate is fragile, the casting can be beaten directly, which can save manpower. The excess mold opening can be reused after melting. The usual yield is about 67%.
3. Die casting application
Die-casting has high production efficiency and can die-cast parts with complex shapes, precise dimensions, clear outlines, high surface quality and strength, and hardness, so it is widely used and developed rapidly. The die-casting process has a wide range of uses and is widely used in the production of daily production equipment and consumer goods. Globally, 60% of die-casting parts are used in automobile manufacturing. For example, various parts of Mercedes-Benz cars also use the die-casting process.